
Konik horses are a re-creation of one of the original types of wild horses. Horses are grazing animals and require a large area in which they can move around and graze constantly if they are to reach optimum health.
How long do horses live.
What kind of ecosystem do horses live in. What ecosystem do horses live in. Horses that are kept in captivity often live in large fields or pastures. There are horses that are suited to almost any climate so they can live nearly anywhere.
They also can live in grasslands across the prairie. They live in Virginia Colorado and a little more. Wild horses are becoming extinct because people are building cities and cutting down trees in thier ecosystem.
Rabbits other horses in their heard and other animals in the dessert all interact with wild horses. Wild horses may fight with wild stallions. Animals in the desert such as elk gray fox and.
Horses are grazing animals and require a large area in which they can move around and graze constantly if they are to reach optimum health. In the wild a horse with undefined boundaries will graze for 16 hours walk up to 20 kilometres per day. A domesticated horse kept at pasture will require at least one hectare of pasture.
Feed supplementation may still be required in summer and winter when. Horses are now also being used for conservation of green spaces rural landscapes and parks. The use of horses in this area is helping to inspire areas to grow back naturally.
This is a part of Urban Rewilding. Just like birds horses also help in the spreading of seeds. The seeds make their way into the digestive tract of horses from fruits.
These then stay in the digestive tract for a few hours while the horse. The horse has been domesticated or tamed and kept by people for many centuries. Through the centuries the horse has proven to be a tough animal.
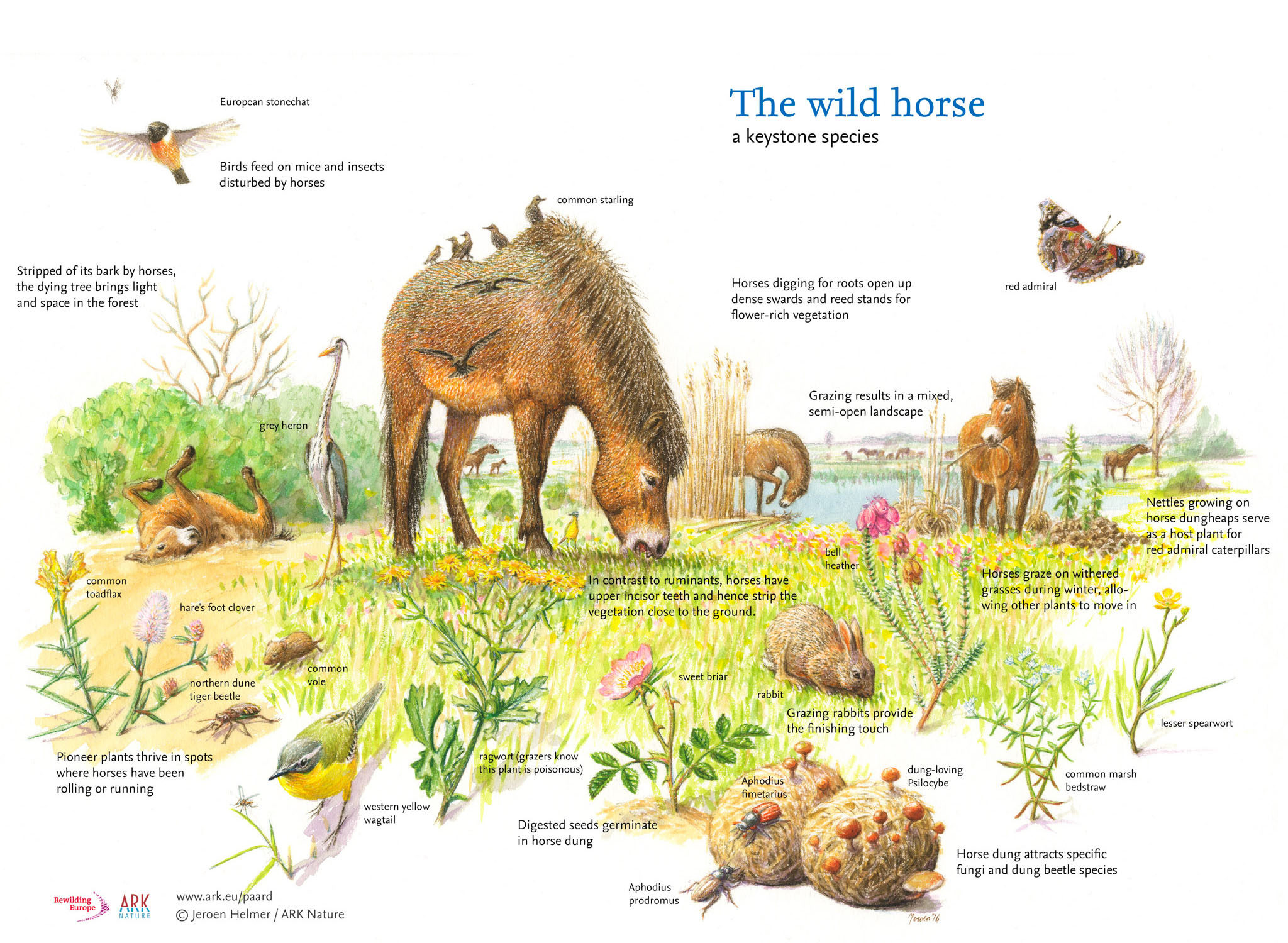
It can live in almost any climate. Horses also build an ecosystems biodiversity. Grazing horses focus on grasses which protects the growth of other plants like flowers.
Plants and flowers also receive assistance from horses through the trampling of uneaten and often unwanted vegetation like weeds. Once the vegetation is dead plants and flowers dont have to compete with it for valuable nutrients water and other resources. What type of animal is a horse.
Horses fall into the Equus genus which comprises animals similar to the domestic horse. Asses and zebras are members of this genus because they are equine creatures. All of these animals are large ungulate mammals which means that they have hoofs.
How long do horses live. Domestic horses live between 25 and 30 years. Free-roaming horses might live.
These 10 characteristics will help you understand why horses are unique. As mentioned above horses are prey animals and are hunted by predators. One of their best methods of defense is to run.
All horses thrive on grass hay herbs and miscellaneous vegetables. Konik horses are a re-creation of one of the original types of wild horses. Many of the English pony breeds are semi-feral because they are allowed to roam freely on common pastures or preserves.
As compared to most pampered domestic breeds these ponies are more resistant to harsh weather and severe winter conditions. They are still adapted to foraging in the wild and capable of. The development of the West however drove wild horses to other locations including deserts.
Desert climates were suboptimal for early horses as they were characterized by rough rocky terrain and limited food and water supplies. However the hardiest horses adapted and wild breeds still live in desert locales. Natural Habitat for Some Wild Horse Breeds.
Shetland ponies inhabit moorland comprising hilly and windy grassy regions in the Scottish Shetland Island. Mustangs roam freely in rough rocky grasslands of western United States. Przewalskis horse Mongolian wild horse live in plains grasslands and grassy deserts of Central Asia.
Wild horses survive in relatively harsh conditions within semi-arid plains deserts prairies grasslands and badlands. They live a semi-nomadic life within a specified square-mile radius depending on the availability of adequate water vegetation and shelter. Desert grasses grow in lower elevations while their remaining vegetative habitat consists of various species of sagebrush and.
We are all familiar with the benefits we derive from horse ownership including the sometimes large contribution these gentle giants make to our physical and mental wellbeing yet benefits accrue to the community as well from having horses in the neighborhood ranging from socioeconomic to environmental. As horse ownership increases throughout the developed world these benefits need to. Horses adapt to their environments by developing helpful physical characteristics such as long broad teeth for chewing flat leaves long ears sensitive to detecting subtle sounds and sturdy hooves and fast legs which help horses run from danger.
Modern horses come in seven distinct species and classify into many different breeds. Some physical features vary among breeds such as weight. Noble patient and reliable horses and ponies have lived and worked with us for over 6000 years.
As herbivore herd animals they are gentler than many other animals. Unlike many other herbivores they are both intelligent and strong. Regarding horse habitat they prefer to live in wide green areas where they can easily access the herbs and plants to eat.
Domesticated horses used for transportation purposes are found in the habitat created for them by their masters and feel comfortable in such environment as they get used to it. They also like places that are near water. Moreover they are also found in lower hilly areas.